Recognizing the Classification and Handling of Different Sorts Of Waste
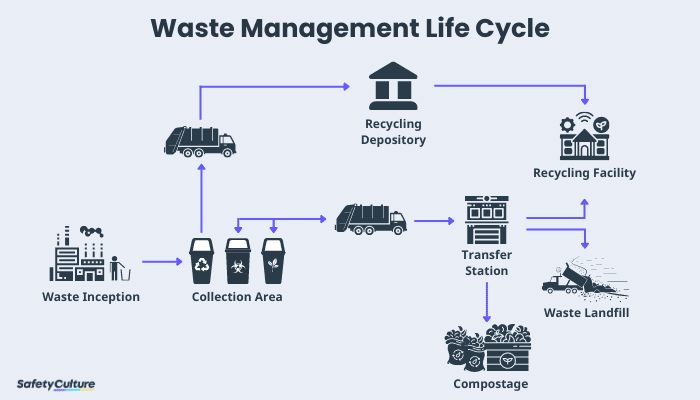
Reliable waste administration is essential for environmental sustainability, requiring a comprehensive understanding of the category and handling of different waste types. Household waste, industrial by-products, unsafe products, electronic refuse, and natural residues each require unique procedures to make sure safety and minimize eco-friendly damage.
Home Waste
House waste, including a wide array of disposed of products generated from everyday living tasks, stands for a significant element of the total waste stream - recycling lives services. This classification consists of organic waste such as food scraps, lawn trimmings, and paper products, along with not natural materials like plastics, steels, and glass. The varied nature of home waste demands efficient classification and administration to minimize environmental impact and advertise lasting living practices
Effective house waste management starts with segregation at the resource, promoting recycling, composting, and risk-free disposal. Organic waste, for circumstances, can be composted to generate nutrient-rich soil modifications, lowering land fill concern and boosting soil wellness. Recyclable products, including paper, glass, and specific plastics, can be processed and repurposed, lowering and saving resources power usage related to brand-new material manufacturing.
Additionally, dangerous household waste such as batteries, digital devices, and cleansing chemicals requires specialized taking care of to avoid dirt and water contamination. Public awareness projects and practical disposal options play essential duties in making sure proper disposal and recycling of these materials. By applying robust waste reduction strategies and promoting area involvement, communities can substantially ease the ecological footprint of family waste.
Hazardous Waste
Industrial waste, a significant contributor to global waste generation, encompasses a diverse range of materials produced by production, building and construction, and other commercial tasks. Effective monitoring of commercial waste is crucial for reducing environmental effect and advertising lasting practices.
The handling of industrial waste generally entails a number of procedures: collection, therapy, disposal, and segregation. Collection systems are made to effectively gather waste products from different resources within an industrial procedure.
Taking on methods such as waste reduction, source recuperation, and recycling can dramatically decrease the worry of hazardous waste on the setting, adding to more sustainable commercial techniques.
Hazardous Waste

The classification of harmful waste is usually based upon its chemical and physical attributes. Hazardous wastes consist of dangerous materials that can create damaging health effects even at reduced concentrations. Corrosive wastes can damage or damage living cells and products. Flammable wastes can conveniently spark, posturing fire hazards, while responsive wastes can trigger surges or launch poisonous gases upon contact with various other materials.
Efficient hazardous waste administration entails several vital methods: recognition and partition of unsafe materials, secure transportation and storage space, and proper therapy and disposal. Therapy methods might include chemical neutralization, stabilization, and incineration. Governing conformity is necessary, directed by structures such as the Source Conservation and Healing Act (RCRA) in the United States, which makes certain environmentally audio and risk-free management of unsafe waste.
Electronic Waste
Electronic waste, typically abbreviated as e-waste, represents an expanding difficulty in waste administration because of the quick obsolescence of innovation. This category includes a broad series of disposed of electronic gadgets, consisting of smart devices, computer systems, televisions, and household home appliances. The intricacy of e-waste depends on its structure; these things contain a mix of important products such as gold and copper, along with dangerous compounds like lead, mercury, and cadmium.

Regulation and policies, such as the European Union's Waste Electronic and electric Equipment (WEEE) Instruction, objective to advertise responsible e-waste administration. These policies mandate makers to help with the collection and recycling of digital products, therefore decreasing the burden on garbage dumps and reducing environmental contamination.
Organic Waste
Organic waste, incorporating eco-friendly materials such as food scraps, yard trimmings, and farming residues, comprises a considerable portion of the municipal solid waste stream. This type of waste is significant not only for its volume yet likewise for its possible environmental influence if not handled properly. Organic waste can decompose anaerobically in garbage dumps, producing methane, a powerful greenhouse gas contributing to environment change.
Proper handling of organic waste includes a number of approaches. Composting is an extensively embraced approach, changing organic materials into useful compost that can improve soil and support sustainable farming. This procedure likewise minimizes the volume of waste sent to land fills. Another method is anaerobic digestion, which breaks down organic issue in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be made use of as a renewable resource source. Additionally, diverting food waste from garbage dumps with donation programs can minimize food instability while decreasing waste.
Municipalities and services are significantly identifying the importance of natural waste monitoring. Implementing detailed organic waste site recycling programs not just minimizes ecological effects but likewise aligns with wider sustainability goals, promoting a round economic situation where sources are continuously reused and repurposed.
Conclusion
Effective waste monitoring and ecological security demand a detailed understanding of the category and handling of numerous waste types. Implementing proper methods for each waste type makes certain safe and liable waste monitoring practices, ultimately adding to the security of communities and public health and wellness.
Reliable waste administration is critical for ecological sustainability, needing a comprehensive understanding of the classification and handling of different waste kinds.Household waste, encompassing a broad variety of thrown out materials generated from daily living activities, represents a substantial part of the overall waste stream.Industrial waste, a major factor to international waste generation, incorporates a varied variety of materials produced by manufacturing, building and construction, and various other commercial activities (recycling lives services).Dangerous waste, a vital problem in waste monitoring, consists of products that position significant risks to human health and the setting due to their toxic, corrosive, combustible, or responsive buildings.Organic waste, incorporating eco-friendly products such as food scraps, lawn trimmings, and farming residues, makes up a considerable this page part of the local strong waste stream